

of neutrons you can subtract the mass number (23) from the atomic number(11)). Every sodium atom has 11 protons, 12 neutrons and 11 electrons. We have learned that the protons, neutrons and electrons of atoms of the same element will be equal. Here are the first 20 elements in the periodic table, that you need to learn, with their respective proton numbers and electronic configurations. The elements in each column have the same number of valence electrons too (check the periodic table below to see if it’s true!). In the periodic table, elements are arranged in order of atomic number. Use atomic (proton) number and the simple structure of atoms to explain the basis of the Periodic Table, with special reference to the elements with atomic (proton) numbers 1 to 20.Sine the electrons have next to no weight, only the protons and neutrons are considered when calculating the mass of the atom. Mass number of nucleon number is the number of nucleons (no. Hydrogen has one proton, so every atom of hydrogen will have a proton number of 1. Every atom of the same element has the same number. Define atomic (proton) number and mass (nucleon) number.Ītomic number or proton number is the number of protons in the nucleus (or the electrons since they’re equal in number!).of positive and negative charges in an atom will be equal- thus, the atom has no overall charge. The no.of protons and electrons in an atom will always be equal, that means that the no. Most of the atom’s weight is in the nucleus, since electrons weigh hardly anything. State the relative charges and approximate relative masses of protons, neutrons and electrons.Ī proton (p) has a relative mass of 1 and a positive (+1) chargeĪ neutron (n) has a relative mass of 1 and has no chargeĪn electron (e) has a negligible (about 0.00054) relative mass and a negative (-1) charge.Thus noble gases do not combine with other elements to form compounds. This electronic structure is called stable, because they cannot lose or gain electrons to take part in chemical reactions.
No meaning in periodic table full#
They have valence electrons that are the maximum number of electrons that can go into their shells (‘He’ has one shell and so has 2 valence electrons, and the rest of the gases in the column have two or more shells, so they have 8 valence electrons), meaning they have full outer shells of electrons. The last column is called group 0 and the elements in it are called noble gases.
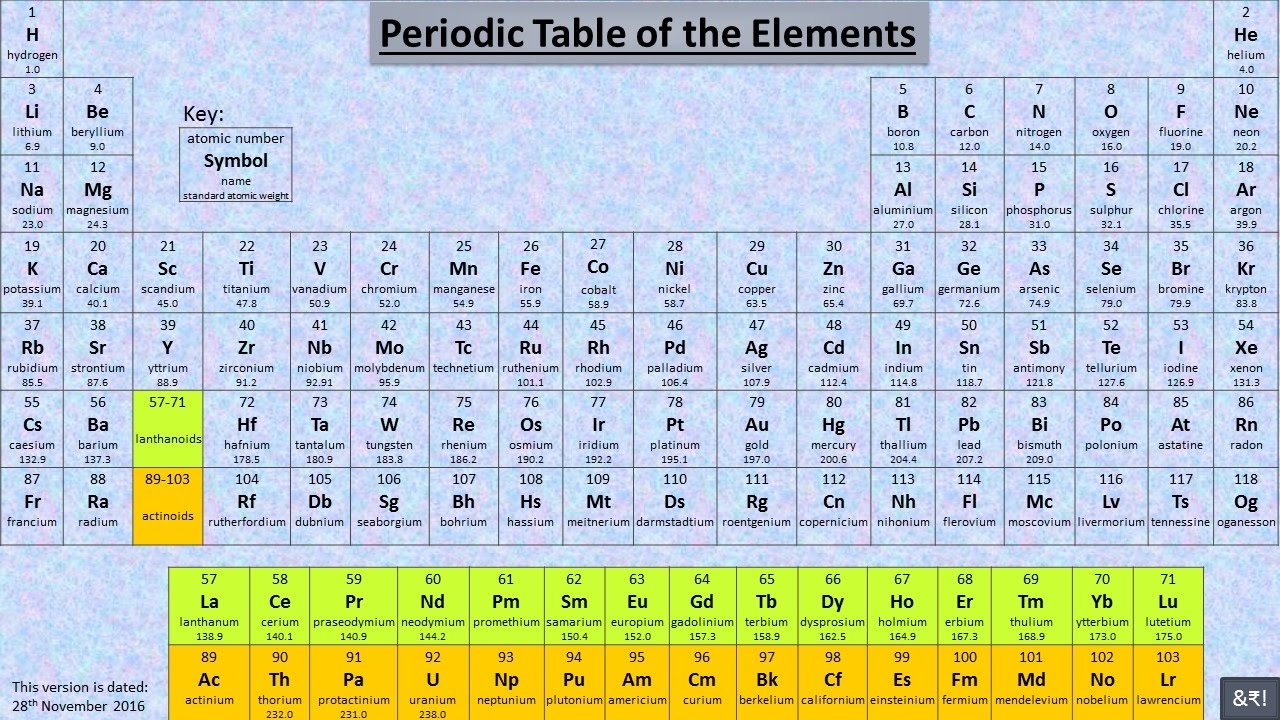
This is a section of the periodic table, the table that contains all the elements that have been discovered by humans. Valence electrons are important, as it determines whether there will be a reaction between particular elements and if yes, what products will be formed as a result. Chemical reactions occur when atoms’ gain or lose electrons- this will be explained in the next topic. The number of electrons in an atom’s outer shell are called valence electrons. This electronic configuration can be written as 2,8,1. In a sodium atom, there are two electrons in the first shell, eight electrons in the second and one in the third.

The arrangement of the electrons in shells is called the electronic structure or electronic configuration. All of the following shells can hold a maximum of eight electrons. The first shell is nearest to the nucleus and can only contain a maximum of two electrons.

We’ve learned that all substances in the world are made up of atoms. Describe the structure of an atom in terms of electrons and a nucleus containing protons and neutrons.We apologise for the inconvenience, but hope that the new images will provide you with an even better learning experience. Disclaimer: Due to unforeseen difficulties, we have had to take down the images on this notes page.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
